Comparators
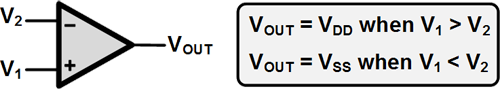
The comparator is a device which compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger.
A standard op-amp can be used as a comparator as indicated in the following diagram.
VOUT = VDD when V1 > V2
VOUT = VSS when V1 < V2
When the non-inverting input (V1) is at a higher voltage than the inverting input (V2), the high gain of the op-amp causes it to output the most positive voltage. When the non-inverting input (V1) drops below the inverting input (V2), the op-amp outputs the most negative voltage.
Example:
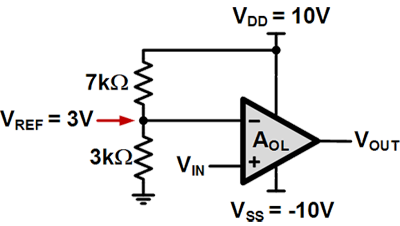
Op-amp comparator can be used as a voltage level detector. The figure below shows a level detector that compares a DC reference voltage (VREF) of 3V to VIN with VDD = 10V and VSS = -10V
When VIN exceeds 3V, VOUT goes to the 10V positive rail due to its high gain open-loop configurations. When it falls below 3V, VOUT flips to the -10V rail.