Feedback
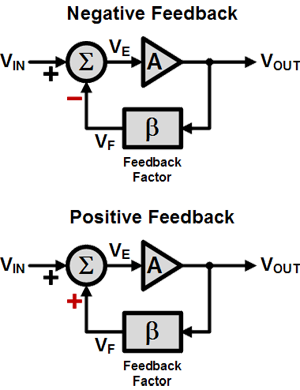
Feedback is a process whereby a fraction of the output signal is sensed (VF) and compared with the input (VIN), generating a very small feedback error term (VE = VIN – VF), thereby making the output an accurate replica of the input.
Example: the typical non-inverting closed loop configuration
It is instructive to identify four elements in the feedback system.
- The feed forward amplifier (A)
- A means of sensing the output
- The feedback network (β)
- A means of generating the feedback error (Σ)
These elements exist in every feedback system. The pictures above describe a general feedback system, showing both negative and positive feedback configurations.
Negative and Positive Feedback
There are two kinds of feedback: negative feedback and positive feedback. If the sensed feedback voltage VF has the same phase with the input voltage, then it is a negative feedback; otherwise, it is positive.
Negative feedback allows high precision signal processing. Positive feedback makes it possible to build oscillators.
Before proceeding to the analysis of feedback circuits, we'll first describe the benefits of the negative feedback:
- Provides gain desensitization. For example, the closed loop gain is much less sensitive to device parameters than the open loop gain.
- Controls the input/output impedance, that is, raise or lower the input and output impedances by the selection of an appropriate feedback topology.
- Increases the amplifier bandwidth.
- Reduces noise by minimizing the contribution, to the output, of unwanted electric signals generated by the circuit components themselves as well as extraneous sources.
- Reduces nonlinear distortion in an amplifier by making the output proportional to the input.